本文共 5770 字,大约阅读时间需要 19 分钟。
9.3BRDF
spatially varing BRDF(SVBRDF):基于空间位置变化的BRDF函数
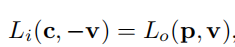
相机c来自v方向的radiance等于v与场景最近交点p点在v方向出射的radiance
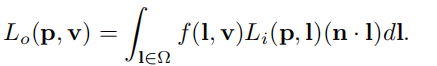
l ∈ Ω l\in\Omega l∈Ω:l在半球上的积分
f ( l , v ) f(l,v) f(l,v):BRDF,出射光的radiance与入射光的radiance之比
注意一点:
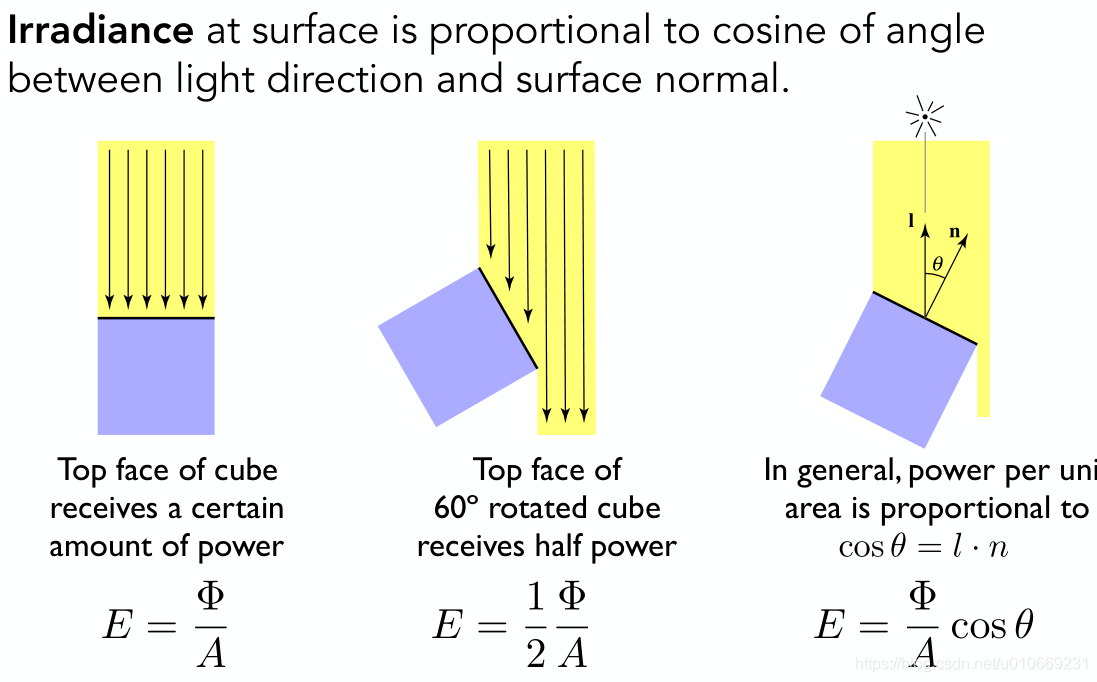
radiance Li 是power received by area dA from “direction” dω
Irradiance: total power received by area dA
所以 n ⋅ l n\cdot l n⋅l意义如下:
RTR4中为了简单,在表述上忽略p
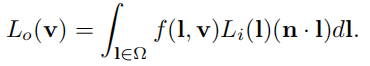
使用球坐标系, c o s θ i = n ⋅ l cos\theta_i=n\cdot l cosθi=n⋅l
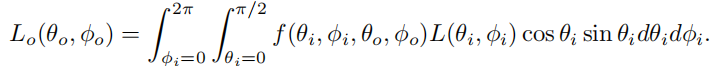
令 u i = c o s θ i u_i=cos\theta_i ui=cosθi u 0 = c o s θ 0 u_0=cos\theta_0 u0=cosθ0,这样 d l = d u i d ϕ i dl=du_id\phi_i dl=duidϕi
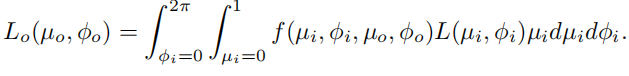
directional-hemispherical reflectance 给定方向到整个半球反射:该函数表明了一个给定方向的入射光向整个半球反射的光的量
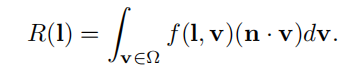
与之对立的是hemispherical-directional reflectance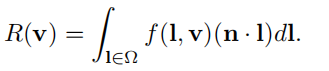
Lambertian模型的BRDF f ( l , v ) f(l,v) f(l,v)是常数,积分得到
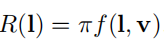
接着得出:
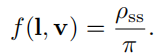
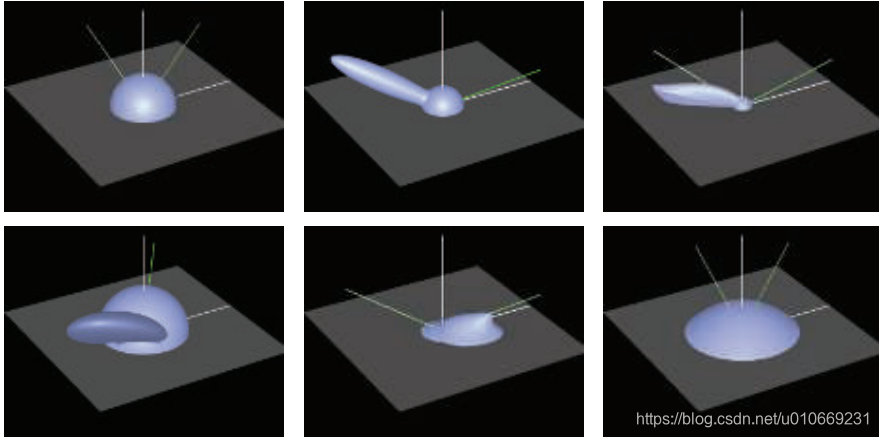
BRDF f ( l , v ) f(l,v) f(l,v)可视化,绿实线为入射光,绿虚线和白线为反射方向。
第一行从左到右:1.Lambertian 2.Blinn-Phong 高光+Lambertian 3.Cook-Torrance BRDF
第二行从左到右:1.Ward的各向异性模型 2回射3.grazing angles
9.4 L i ( ) L_i() Li()
punctual lights
具有位置(location)的光,区别于平行光。punctual lights没有形状、尺寸,和真实世界的光源不同。术语"punctual"和守时没有关系,而是来自拉语punctus,意思是"point",指从单个位置发光的光源。两种punctual lights:点光源(point light)和聚光灯(spotlight)
对反射方程积分得到
( ) + ()^+ ()+:小于0截断
π \pi π:消除BRDF经常出现的 1 π \frac{1}{\pi} π1系数
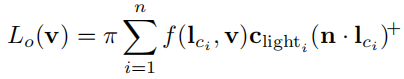
方向光
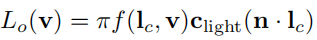
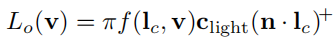
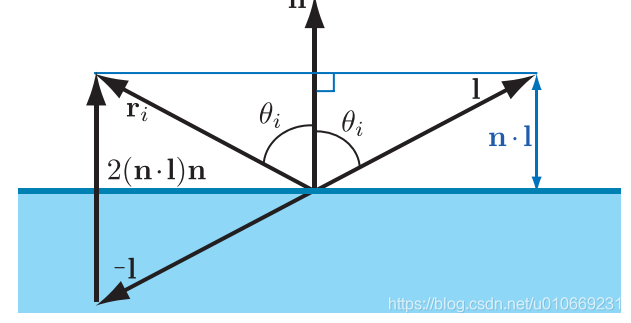
反射方程 − n ⋅ l + 2 ( n ⋅ l ) n -n\cdot l+2(n\cdot l)n −n⋅l+2(n⋅l)n
斯涅耳定律
n 1 n_1 n1入射反射光所在的一边, n 2 n_2 n2折射光在的一边
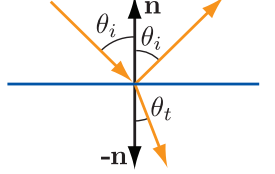
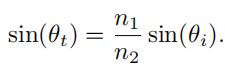
Fresnel现象:光线的反射率与视角相关的现象
完整的菲涅尔方程相对复杂,解决方法是用更少的参数近似。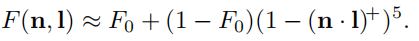
需要的参数仅为 F 0 F_0 F0,当光线垂直撞击表面时,该光线被反射为镜面反射光的比率被称为F0
计算方法如下:
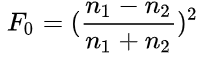
空气中 n 1 n_1 n1近似为1
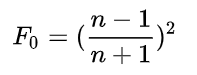
更广泛的近似,参数多了两个,p可以用来近似特定的材质, F 90 F_{90} F90用来近似那些Schlick方程匹配较差的材质。
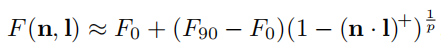
NDF
the distribution of normals,法线密度的分布函数,以下图所示微表面模型为例:
该表面的NDF如下
N D F ( m ) = { 2 2 m = m 1 2 2 m = m 2 0 m = o t h e r NDF(m)=\begin{cases} \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}&m=m_1\\ \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}&m=m_2\\ 0&m=other \end{cases} NDF(m)=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧22220m=m1m=m2m=other
m是指微表面的法线,n只整个区域的法线,上式的意思是微表面法线为m1,m2的密度为 2 2 \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} 22,其他区域为0,这个patch的面积为1
可以得到以下几点
1, 0 < = D ( m ) < = + ∞ 0<=D(m)<=+\infty 0<=D(m)<=+∞微表面法线密度始终为非负值
2,微表面的总面积始终不小于宏观表面总面积,微表面完全为平面时等于patch的面积1。在本例中微表面的总面积为 2 \sqrt{2} 2
∫ D ( m ) d m = Σ i = 1 2 D ( m i ) = 2 2 + 2 2 = 2 \int D(m)dm=\Sigma_{i=1}^2D(m_i)=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}=\sqrt{2} ∫D(m)dm=Σi=12D(mi)=22+22=2
∫ D ( m ) d m > = 1 \int D(m)dm>=1 ∫D(m)dm>=1
3.任何方向上微观表面投影面积始终与宏观表面投影面积相同,本例假定视线v平行m1
∫ D ( m ) ( v ⋅ m ) d m = 2 2 × 0 + 2 2 × 1 = 2 2 = v ⋅ n \int D(m)(v\cdot m)dm=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\times0+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\times 1=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}=v\cdot n ∫D(m)(v⋅m)dm=22×0+22×1=22=v⋅n
4. ∫ D ( m ) ( n ⋅ m ) d m = Σ i = 1 2 D ( m i ) = 2 2 ⋅ 2 2 + 2 2 ⋅ 2 2 = 1 \int D(m)(n\cdot m)dm=\Sigma_{i=1}^2D(m_i)=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\cdot \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\cdot \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}=1 ∫D(m)(n⋅m)dm=Σi=12D(mi)=22⋅22+22⋅22=1
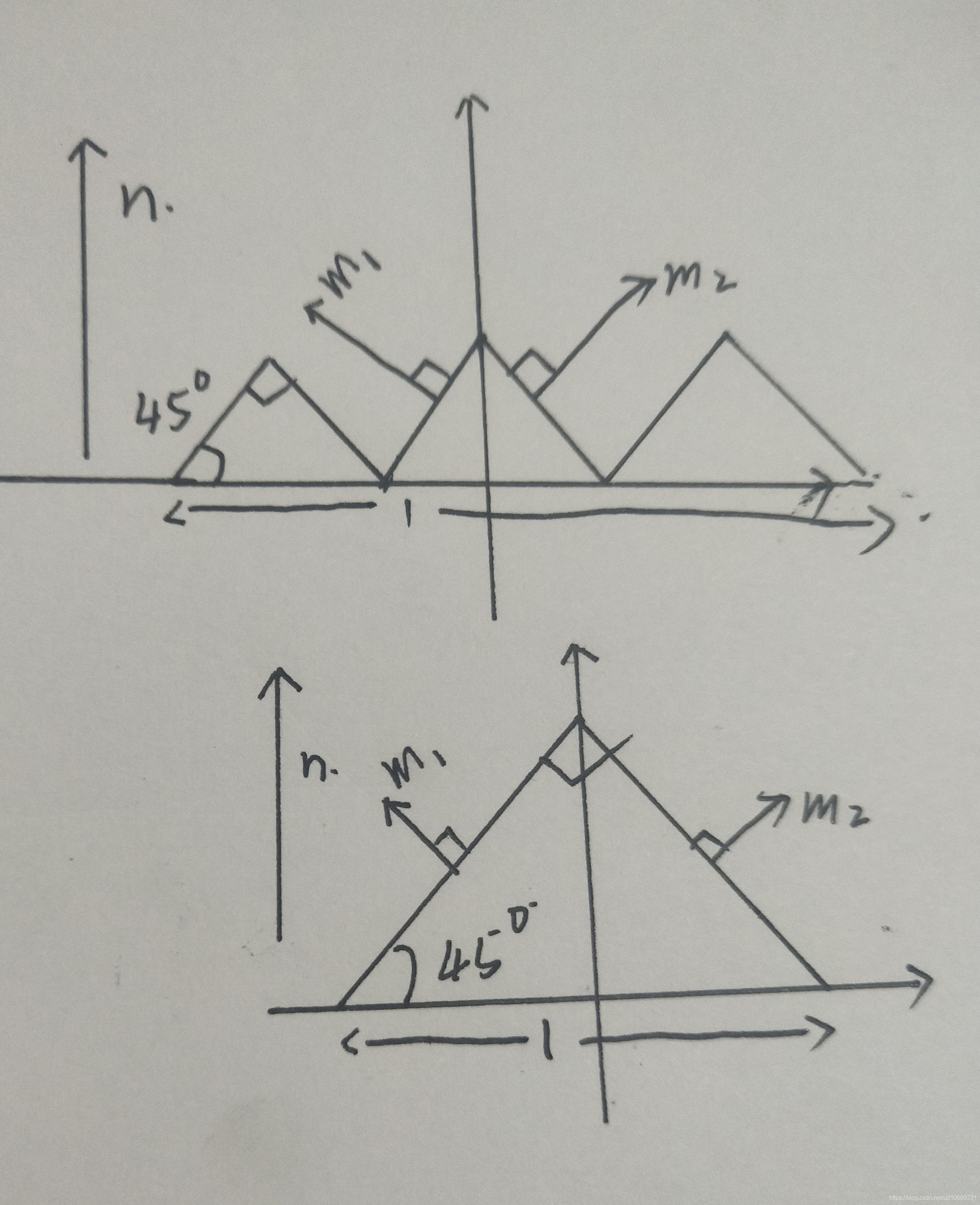
在着色计算时,半向量为h,我们直接将 m = h m=h m=h带入(记住m为微表面的法线),因为其他朝向的h对BRDF没有贡献。
以GTR分布为例,当带入的h很接近n的时候,NDF会给出一个较大的值,即高光区中心部分,当远离h时,NDF逐渐变小,从高光区尾部逐渐变到漫反射区域。
几何衰减系数
(源自:3D游戏与计算机图形学中的数学方法)
两种衰减:
1.某一微表面反射的光被另一表面阻挡
2.光线射入时,部分光线被阻挡
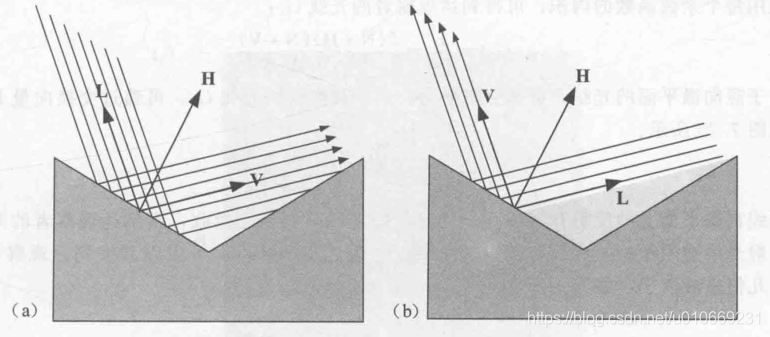
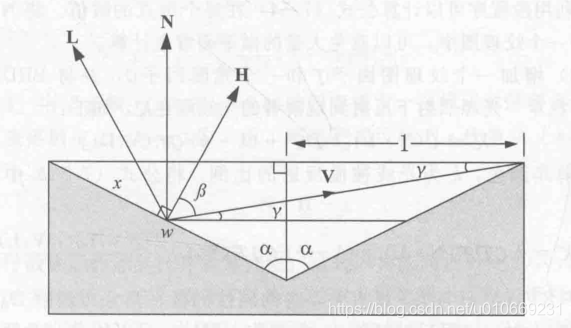
该种微表面模型的衰减函数推导
现在我们计算某一微表面反射的光被另一表面阻挡的程度,也就是x比w的值,记为G1。
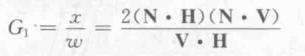
第二种遮挡情况记为G2
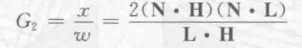
整个函数为
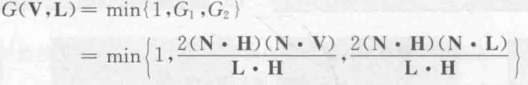
NDF只给出了表面的法线分布情况,并没有确定出微表面模型,同一个NDF的微表面模型,它们的遮挡情况可能是不同的。
Smith遮蔽函数
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/81708753
下面几条是我摘出来有利于后面理解几何衰减函数怎么改进的性质。
1.Smith遮蔽函数(Smith masking function),该函数最初是为高斯正态分布导出的,后来推广到任意NDF
2.Smith G1函数的形式如下:
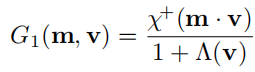
3.其中 χ + \chi^+ χ+为符号函数
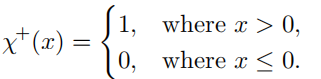
4. Λ \Lambda Λ是从给定的NDF推导而来,在[Walter 2007]和[Heitz 2014]中有描述推导出给定NDF的 Λ \Lambda Λ的过程
5. Λ ( v ) \Lambda(v) Λ(v)表示微表面斜率上的积分
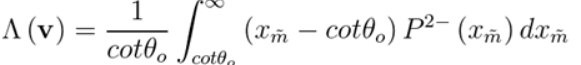
6.Smith遮蔽函数是常见遮蔽函数中,唯一既满足能量守恒又具有法线遮蔽独立性(Normal/Masking Independence)便利特性的函数。法线遮蔽独立性是在以下假设得出,即在微表面的一个点处的高度(或法线)与任何相邻点处的高度(或法线)之间没有相关性,下图右边模型
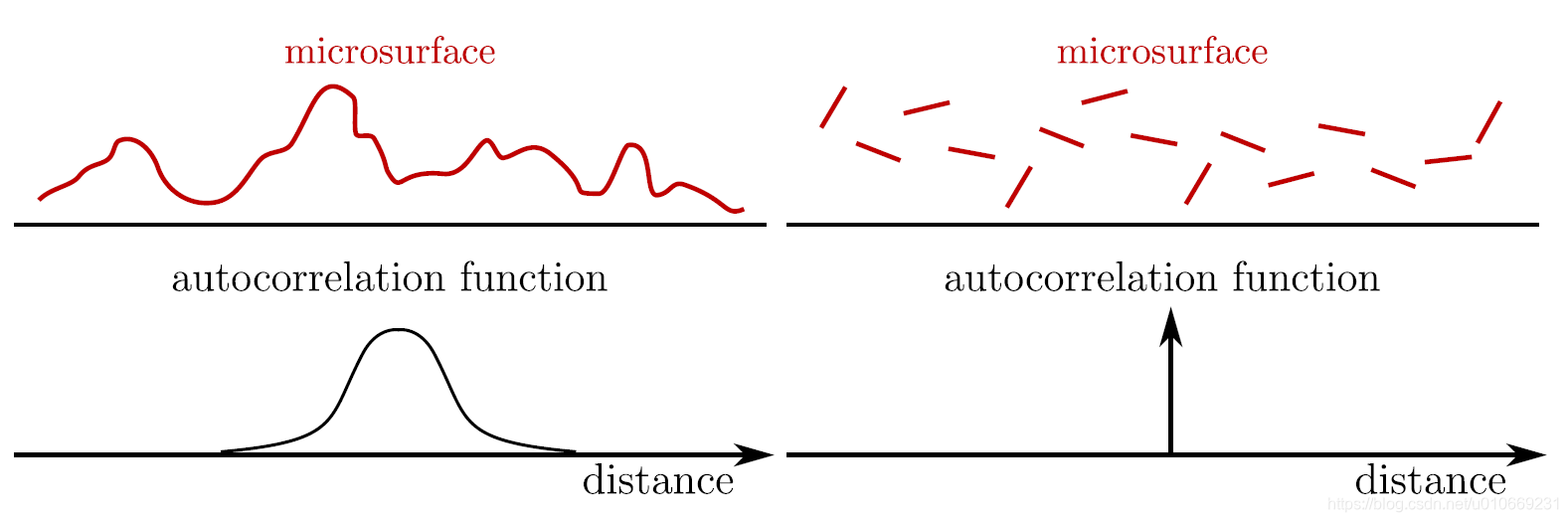
注意masking函数和shadow函数分别对应了最开始推导时的两种衰减情况,即射入光线被阻挡的情况和反射光线被阻挡的情况,这两种情况共同组成了几何衰减函数,最初的推导和masking、shadow function是理解几何衰减函数的重要基础,不然就不知道后面为什么要改进。
直接将射入光线被阻挡函数与反射光线被阻挡函数相乘得到了最简单的分离式 Masking and Shadowing Function。
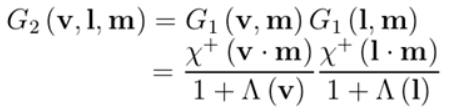
而之前推导的衰减函数取的是最小值 m i n ( G 1 , G 1 ) min(G_1,G_1) min(G1,G1),这意味现在的这个函数 ( G 1 × G 1 ) (G_1\times G_1) (G1×G1)相比来说使得场景更暗!
这个函数认为shadow和masking函数是无关的,极端地想,当视线和光线重合时,入射光线不可能被阻挡,因为此时看不到阴影,没有阴影区域,所以showing函数为结果为1,只考虑反射光被遮挡的情况,最终 G 2 = G 1 G_2=G_1 G2=G1,也就是 m i n ( G 1 , 1 ) min(G_1,1) min(G1,1).分离式函数结果却是 G 2 = G 1 × G 1 G_2=G_1\times G_1 G2=G1×G1,显然错误。
Direction-Correlated Masking and Shadowing
我们需要一个函数来确定masking和shadowing的关系,从第一个推导和分离式函数可以知道,当完全两者完全不相关时,它们的关系是 G 2 = G 1 G 1 G_2=G_1G_1 G2=G1G1,当在另一个极端情况时,它们的关系是 G 2 = m i n ( G 1 , G 1 ) G_2=min(G_1,G_1) G2=min(G1,G1)。
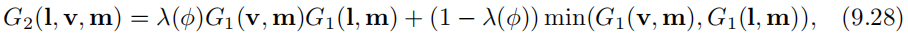
故此我们将两种情况结合起来,用 λ ( ϕ ) \lambda(\phi) λ(ϕ)表示它们的相关程度。 ϕ \phi ϕ为l和v之间的相对方位角。下面是两种表达式:
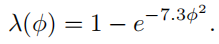
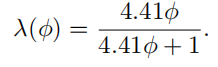
Height-Correlated Masking and Shadowing Function
除了l和v之间的关系外,如果一个点很低的话,那么处在阴影中的概率(shadow)和被遮挡的概率(masking)都会很大,下面的这个函数则考虑了该情况的影响,与最简单的分离式相比就是分母少了个 Λ ( l ) Λ ( v ) \Lambda(l)\Lambda(v) Λ(l)Λ(v),在前面我们有知道 Λ ( v ) \Lambda(v) Λ(v)表示微表面斜率上的积分。
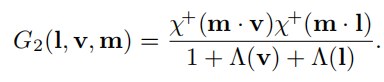
Height-Direction-Correlated Masking and Shadowing Function
如果既考虑高度有考虑方向就得到下面的式子
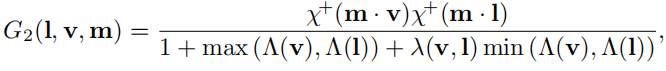
NDF
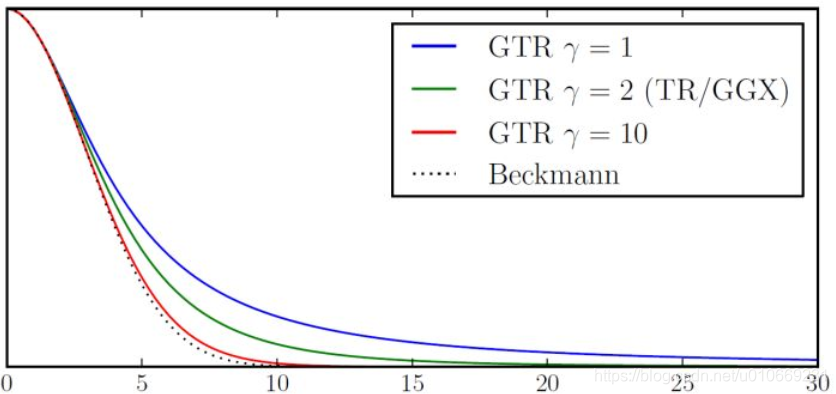
下面列四个NDF,分别是Blinn-Phone NDF,Beckmann NDF,GGX,其余的比如GTR不列了,列多了反而容易混。从各种方面的对比来看GGX都完全碾压另外两个,当然blinn的优点是代价小,这也使得它在一些场景有应用,比如移动设备。
Blinn-Phone NDF
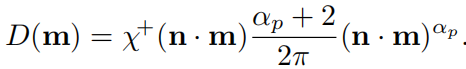
Beckmann NDF
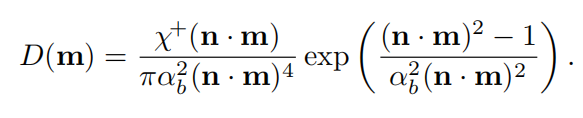
GGX
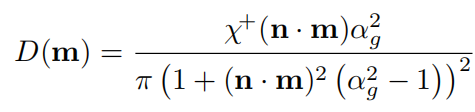
形状分布对比
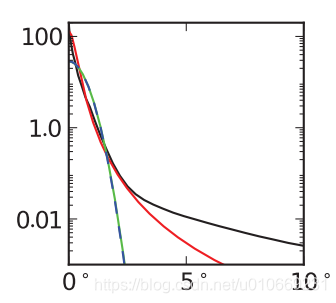

绿色线Blinn-Phone,红色线beckmann,黑色线GGX,相对于beckmann,GGX的拖尾更长,Blinn则几乎没有。而在现实世界中的拖尾一般都长于GGX,这也是GGX受欢迎的原因。
参数与粗糙度的对应
在beckman中,参数 α b \alpha_b αb控制粗糙度。
在Blinn中参数 α p \alpha_p αp可以任意大,主要原因就是它不是线性的,有时一点调整就会造成巨大的粗糙度的改变,而有时则反之,为了解决该问题,在参数和粗糙度之间引入一个映射, α p = m s \alpha_p=m^s αp=ms,s在0到1之间,m是 α p \alpha_p αp的上界。
对于GGX,blurey提出以下映射 α g = r 2 \alpha_g=r^2 αg=r2,r是0-1之间控制粗糙度的参数,这样使得粗糙度以一种线性发生变化。
shape-invariant(形状不变性?) Heitz定义到:如果一个各向同性的NDF是shape-invariant的话,那么缩放粗糙度参数相当于通过倒数拉伸微观几何
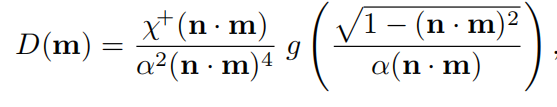
具有形状不变形的函数可以写为上面的形式,该性质带来的优点是可以推导出各项异性的NDF,见下面的式子。形状不变性的第二个优点是可以比较容易推导出几何衰减项。
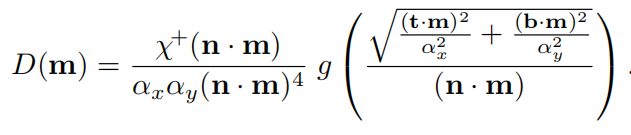
形状不变性优点1:有利于推导各项异性NDF
Blinn不具有形状不变性,故不能推导出。
BeckmannNDF的各向异性版本
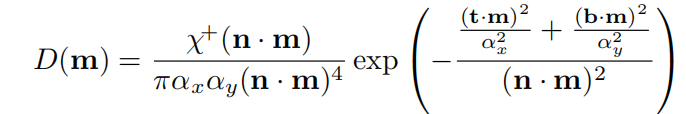
GGX NDF的各向异性版本
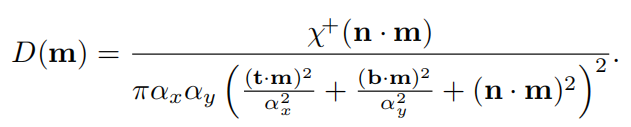
形状不变性优点2:有利于推导出几何衰减项
对于具备形状不变性的函数来说, Λ \Lambda Λ函数只与a有关,在各向同性情况下,它由下式得到
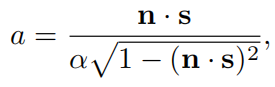
在各向异性中,变成下式
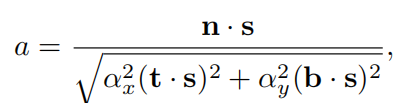
Beckmann中 Λ \Lambda Λ向对于a的函数
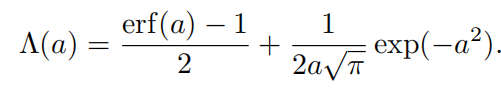
该式存在的问题是erf(erro function)和exp计算起来消耗都有点大,下面是该函数的近似版本
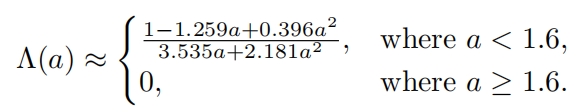
GGX中 Λ \Lambda Λ向对于a的函数
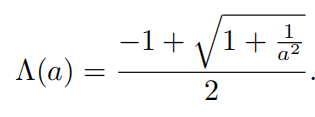
GGX优化:
由于GGX的广泛使用,所以人们提出了很多方法来简化GGX的计算,主要方法其实就是把GGX推导出的几何衰减函数G和BRDF分母的那两项进行约分来减少计算。
对 height-correlated Smith G2的简化
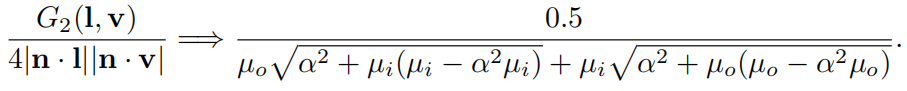
GGX对G1的简化
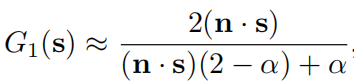
如果采用上面的这种形式,height-correlated Smith G2可以变得更简单
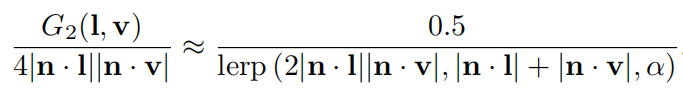
转载地址:http://tfuh.baihongyu.com/